
roller guides
Roller guides, essential components in various applications, facilitate smooth linear motion. These guides, capable of supporting loads from all directions, come in diverse types like flat, Gothic arch, and V-type designs.
What are Roller Guides?
Roller guides are precision mechanical components designed to constrain and direct linear motion, utilizing rolling elements – typically cylindrical rollers – to minimize friction. Unlike sliding friction guides, roller guides employ rolling friction, resulting in significantly reduced wear, higher efficiency, and increased load capacity. They are fundamental in systems requiring accurate and repeatable linear movements.
These guides aren’t merely about movement; they’re about supporting loads from all directions, offering stability and precision. Different types exist, including flat, Gothic arch, V-type, C-Line (Type LS), and Heavy-Line (type GU, GP), each tailored for specific applications and load requirements. Their construction allows for smooth operation even under substantial weight, making them invaluable in diverse industries and recreational activities.
Essentially, roller guides transform linear motion into a more efficient and reliable process, extending the lifespan of machinery and enhancing performance.
The History of Roller Guide Development
The evolution of roller guides is intertwined with the broader history of linear motion technology. Early forms of linear guidance relied on simple sliding surfaces, prone to wear and friction. The conceptual shift towards rolling elements began with advancements in bearing technology during the Industrial Revolution, though dedicated roller guides as we know them emerged later.
The mid-20th century witnessed significant development, driven by demands for precision in manufacturing and automation. Innovations focused on optimizing roller geometry – leading to designs like Gothic arch and V-type guides – and material science, enhancing durability and load capacity.
Fila Skates’ SoftWear technology, applied to Fitness Line roller skates, exemplifies a modern application influencing guide design. Simultaneously, industrial needs spurred the creation of Heavy-Line types (GU, GP) for robust applications. Today, ongoing research centers on minimizing friction, maximizing lifespan, and adapting roller guides for emerging technologies.

Types of Roller Guides
Roller guides encompass several designs, including flat, Gothic arch, V-type, C-Line (Type LS), and Heavy-Line (Types GU, GP), each suited for specific applications and load requirements.
Flat Roller Guides: Design and Applications
Flat roller guides represent a foundational type within linear motion systems, characterized by their simple yet effective design. These guides typically consist of a flat rail surface and cylindrical roller elements that travel along it, providing smooth and precise movement. Their construction allows for load distribution across a wider area, enhancing stability and reducing stress concentration.
The primary application of flat roller guides lies in scenarios demanding moderate load capacity and accuracy. They are frequently employed in automated machinery, conveyor systems, and various industrial equipment where consistent linear motion is crucial. Furthermore, their relatively straightforward design contributes to cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for numerous manufacturing processes. They are also found in some fitness equipment, supporting the smooth rolling action of inline skates, as part of the broader roller skating world.
However, it’s important to note that flat roller guides may exhibit limitations when subjected to extremely heavy loads or high precision requirements compared to more specialized types.

Gothic Arch Roller Guides: Features and Benefits
Gothic arch roller guides distinguish themselves through a unique roller element design, shaped like a Gothic arch. This distinctive geometry significantly enhances load-carrying capacity and provides superior performance compared to traditional flat roller guides. The arched shape allows for multiple contact points between the roller and the rail, distributing the load more evenly and minimizing deformation under stress.
A key benefit of Gothic arch roller guides is their ability to handle both radial and thrust loads effectively. This makes them ideal for applications involving complex movements and varying force directions. They excel in high-precision machinery, robotics, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment where accuracy and reliability are paramount. The design also contributes to quieter operation and reduced friction, extending the lifespan of the system.
While generally more expensive than flat roller guides, the enhanced performance and durability of Gothic arch designs often justify the investment in demanding applications.
V-Type Roller Guides: Specific Uses
V-type roller guides, characterized by their V-shaped raceways and corresponding roller elements, are specifically engineered for applications demanding high rigidity and precision. These guides excel in environments subject to significant vibration or shock loads, offering exceptional stability and load-bearing capabilities. The V-groove design inherently provides self-alignment, compensating for minor misalignments during installation or operation.
Specific uses for V-type roller guides are prevalent in machine tool construction, particularly in CNC milling machines and lathes. They are also frequently found in automated machinery, robotics, and material handling systems where precise positioning and smooth movement are critical. Their robust construction makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications, supporting substantial weights with minimal deflection.
Furthermore, V-type designs are often favored in applications requiring frequent start-stop cycles, as they exhibit excellent dynamic performance and resistance to wear. They represent a reliable solution for demanding industrial tasks.
C-Line Roller Guides (Type LS)
C-Line roller guides, specifically Type LS, represent a versatile solution within the broader family of linear motion systems. These guides are distinguished by their compact design and high load capacity, making them ideal for applications where space is limited but performance demands are substantial. The ‘C’ designation often refers to the guide’s cross-sectional shape, optimized for efficient load distribution and structural integrity.
Type LS guides are frequently employed in automated machinery, packaging equipment, and various industrial automation processes. Their robust construction ensures reliable operation even under challenging conditions, including exposure to dust, debris, or moderate temperature fluctuations. They offer smooth, precise linear motion with minimal friction, contributing to increased efficiency and reduced wear.
The design of C-Line guides prioritizes ease of installation and maintenance, simplifying integration into existing systems. They are a cost-effective choice for a wide range of linear motion applications.
Heavy-Line Roller Guides (Types GU, GP)
Heavy-Line roller guides, encompassing Types GU and GP, are engineered for demanding applications requiring exceptional load-bearing capabilities and rigidity. These guides excel in scenarios involving substantial forces, high dynamic loads, or significant moments. The robust construction and specialized roller arrangements distinguish them from lighter-duty alternatives.
Types GU and GP are commonly found in machine tools, robotics, and heavy industrial equipment where precision and reliability are paramount. They provide superior stability and resistance to deflection, ensuring accurate and consistent linear motion even under extreme conditions. The design minimizes vibration and noise, contributing to a smoother and more controlled operation.
These guides often feature hardened steel components and precision-ground surfaces to maximize durability and extend service life. Their robust nature makes them a preferred choice for applications where downtime and maintenance costs must be minimized.

Materials Used in Roller Guide Construction
Steel roller guides offer unmatched strength and durability, while polymer roller guides provide a lightweight alternative with excellent corrosion resistance for varied environments.
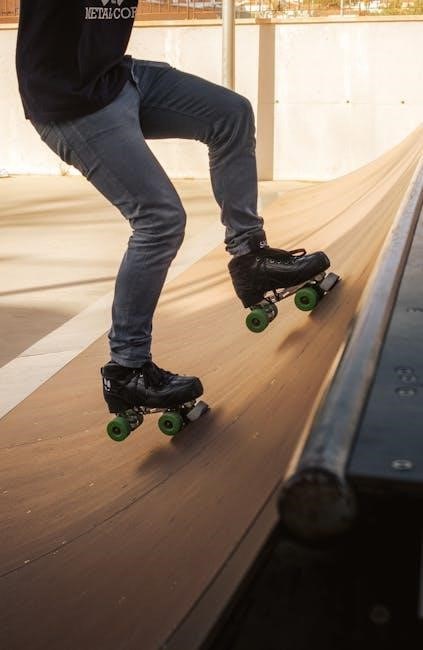

Steel Roller Guides: Strength and Durability
Steel roller guides represent a cornerstone in applications demanding robust performance and longevity. Their inherent strength allows them to withstand substantial loads and impacts, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial machinery and demanding fitness equipment like aggressive inline skates. The material’s high hardness resists wear and deformation, ensuring consistent precision and a prolonged operational lifespan.
Furthermore, steel’s excellent rigidity minimizes deflection under stress, contributing to accurate and reliable linear motion. This is particularly crucial in applications where maintaining tight tolerances is paramount. While susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, advancements in surface coatings and alloy compositions – such as stainless steel options – significantly enhance their resistance to environmental factors.
The manufacturing processes for steel roller guides, including precision grinding and heat treatment, further optimize their mechanical properties. This results in components capable of delivering exceptional performance and reliability even in the most challenging conditions, solidifying steel as a preferred material for critical roller guide applications.
Polymer Roller Guides: Lightweight and Corrosion Resistance
Polymer roller guides offer a compelling alternative to steel, particularly in environments where weight reduction and corrosion resistance are critical. Constructed from materials like nylon, Delrin, or specialized engineering plastics, these guides significantly decrease overall system weight, enhancing efficiency and reducing inertia in applications such as fitness equipment – notably, the Fitness Line of roller skates emphasizing lightweight design.
Unlike steel, polymers are inherently immune to rust and corrosion, making them suitable for use in humid, wet, or chemically aggressive environments. This eliminates the need for protective coatings and reduces maintenance requirements. While generally possessing lower load-bearing capacity compared to steel, advancements in polymer technology have yielded materials with improved strength and wear resistance.
Polymer guides also offer inherent damping properties, reducing noise and vibration during operation. Their self-lubricating characteristics further minimize friction and wear, contributing to smooth and quiet linear motion. This combination of benefits makes polymer roller guides an increasingly popular choice for a wide range of applications.
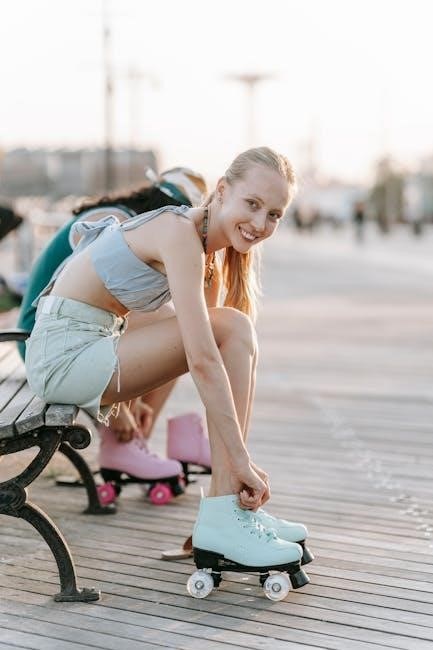
Applications of Roller Guides
Roller guides are vital in roller skating for performance, and find extensive use in industrial applications, enabling precise linear movement in machinery and automation systems.
Roller Skating and Fitness
Roller guides play a crucial role in the performance and maneuverability of roller skates, particularly within the Fitness Line series designed for athletic individuals. This technology, exemplified by Fila Skates’ SoftWear, enhances the skating experience, providing a responsive and comfortable ride for those dedicated to maintaining fitness through skating.
Skating destinations worldwide, like Paris and London, offer ideal environments to experience the benefits of well-functioning roller guides. Whether navigating urban streets or enjoying dedicated skating spots, the quality of these components directly impacts control and efficiency. From leisurely pursuits to intense training, roller guides contribute significantly to the enjoyment and effectiveness of roller skating as a fitness activity.
The ability to confidently explore locations like the Falkland Islands, or participate in events like the Moscow-Elbrus-Transit, relies on the reliability and performance of the roller guide system.
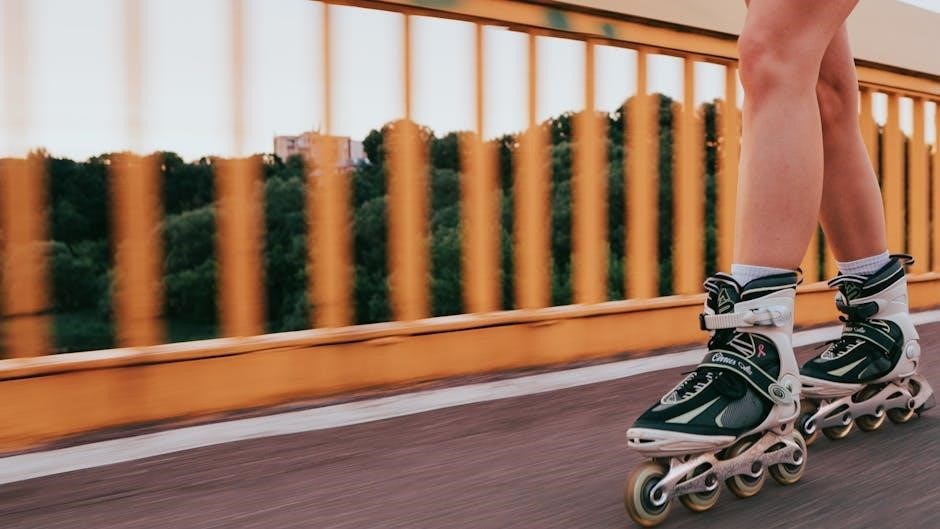
Industrial Applications of Roller Guides
Beyond recreational uses, roller guides are indispensable in numerous industrial applications demanding precision and load-bearing capacity. Their ability to support loads from all directions makes them ideal for complex machinery and automated systems. Various types, including flat, Gothic arch, and V-type roller guides, cater to specific industrial needs.
These guides facilitate smooth and accurate movement in equipment ranging from manufacturing robots to conveyor systems. The robust construction, often utilizing steel roller guides for strength and durability, ensures reliable performance even in harsh operating environments. Precise linear motion, enabled by these components, is critical for maintaining product quality and optimizing production efficiency.
While not explicitly detailed in provided text, it’s understood that consistent performance and minimal maintenance are paramount in industrial settings, making quality roller guides a vital investment.

Maintenance and Longevity
Ensuring roller guide performance requires regular cleaning and lubrication. Addressing issues promptly—troubleshooting common problems—extends the lifespan and maintains optimal functionality.
Cleaning and Lubrication of Roller Guides
Roller guide maintenance hinges on consistent cleaning and lubrication practices. Accumulated debris, such as dust, dirt, and grit, can significantly impede smooth operation and accelerate wear. Regular cleaning, utilizing a soft cloth and appropriate solvent (consult manufacturer guidelines), removes these contaminants.
Lubrication is equally crucial. The correct lubricant minimizes friction, reduces noise, and protects against corrosion. Selecting the appropriate lubricant depends on the roller guide material, load, and operating environment. Lithium-based greases are commonly used, but synthetic options offer superior performance in extreme conditions.
Apply lubricant sparingly, focusing on the rolling elements and raceways. Avoid over-lubrication, as excess lubricant attracts more debris. Establish a regular lubrication schedule based on usage frequency and environmental factors. Inspect roller guides periodically for signs of wear or damage during cleaning and lubrication, addressing any issues promptly to maximize longevity and maintain optimal performance.

Troubleshooting Common Roller Guide Issues
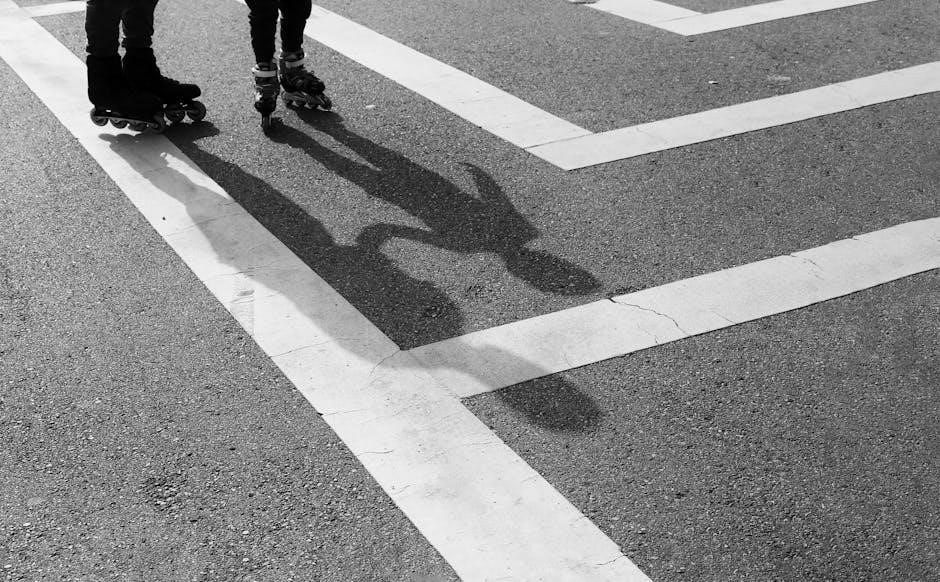

Several issues can affect roller guide performance. Sticking or binding often indicates contamination or insufficient lubrication. Thorough cleaning and re-lubrication are the initial steps. Excessive noise can signal worn rolling elements or damaged raceways, requiring inspection and potential replacement.
Vibration may stem from improper mounting or misalignment. Verify secure attachment and correct alignment using precision measuring tools. Reduced accuracy suggests bearing wear or damage, necessitating component replacement. Inspect for corrosion, particularly in humid environments, and address it with appropriate protective measures.
If problems persist, consult the manufacturer’s documentation or a qualified technician. Regular preventative maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication, and inspection, minimizes the likelihood of these issues. Addressing problems promptly prevents further damage and extends the lifespan of your roller guide system, ensuring continued smooth and reliable operation.

Roller Guide Locations & Destinations
From Paris to Oakland, and even the Falkland Islands, roller skating thrives! Enthusiasts explore diverse locales, enjoying both urban streets and scenic routes worldwide.
Popular Roller Skating Spots Worldwide
The world offers a fantastic array of locations for roller skating enthusiasts, catering to all skill levels and preferences. Paris, often hailed as a roller skating paradise, boasts smooth pavements and a vibrant skating culture, attracting skaters from across the globe. London also presents numerous inviting streets for urban skating adventures.
Venturing further afield, Oakland provides a dynamic skating scene, while destinations like the Falkland Islands, though perhaps less conventional, offer unique and breathtaking backdrops for a skate. SkateFresh’s 2005 journey through Holland showcases the country’s suitability for rollerblading, with expansive routes and picturesque scenery.
Even ambitious expeditions like the Moscow-Elbrus-Transit demonstrate the versatility of roller skating, proving its capability beyond recreational settings. Online forums, like the one mentioned with 7846 topics and 100369 messages, serve as valuable resources for discovering local spots and connecting with fellow skaters, fostering a global community.
Falkland Islands & Roller Skating
The Falkland Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the South Atlantic, present a unique, albeit challenging, environment for roller skating. This archipelago, encompassing East Falkland, West Falkland, and 776 smaller islands spanning 4,700 sq mi (12,000 km2), offers dramatic landscapes and expansive, though often windswept, terrain.
While not traditionally recognized as a roller skating hotspot, the islands’ relatively sparse population and open spaces could appeal to adventurous skaters seeking solitude and unconventional routes. The internal self-governance of the Falklands suggests a potential for developing skating infrastructure, though currently, information regarding dedicated skating facilities is limited.
The islands’ location on the Antarctic-Patagonian platform and proximity to Argentina (known as Islas Malvinas) add to their distinct character. Skating here would be an experience defined by natural beauty and a sense of remote exploration, a far cry from the bustling streets of Paris or London.